The Matching settings determine how strong a question influences the result list in the recommendation phase of your Product Guide in comparison to other questions in your guide. This page gives you an overview of the available settings, explains the main concepts of matching and filtering in the Workbench and finally provides several examples to explain possible outcomes when using these settings.
Table of Contents:
Workbench Settings
Question vs. Answer Option Setting
This page show you the difference between the Question (left) and the Answer Option (right) settings.
Question Detail View
The image below shows you the Detail View for a Question within the Concept Board:
Answer Option Detail View
The image below shows you the Detail View for an Answer Option within the Concept Board:
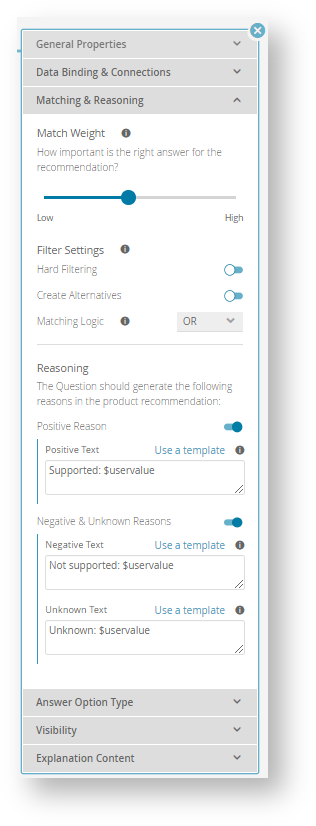
Match Weight
The match weight determines how important the given question is for calculating the product order within the result list.
Therefore, the workbench allows you to set the match weight as low-medium-high by a slider as shown in the image below.
Use Case
(see Matching Use Case below).
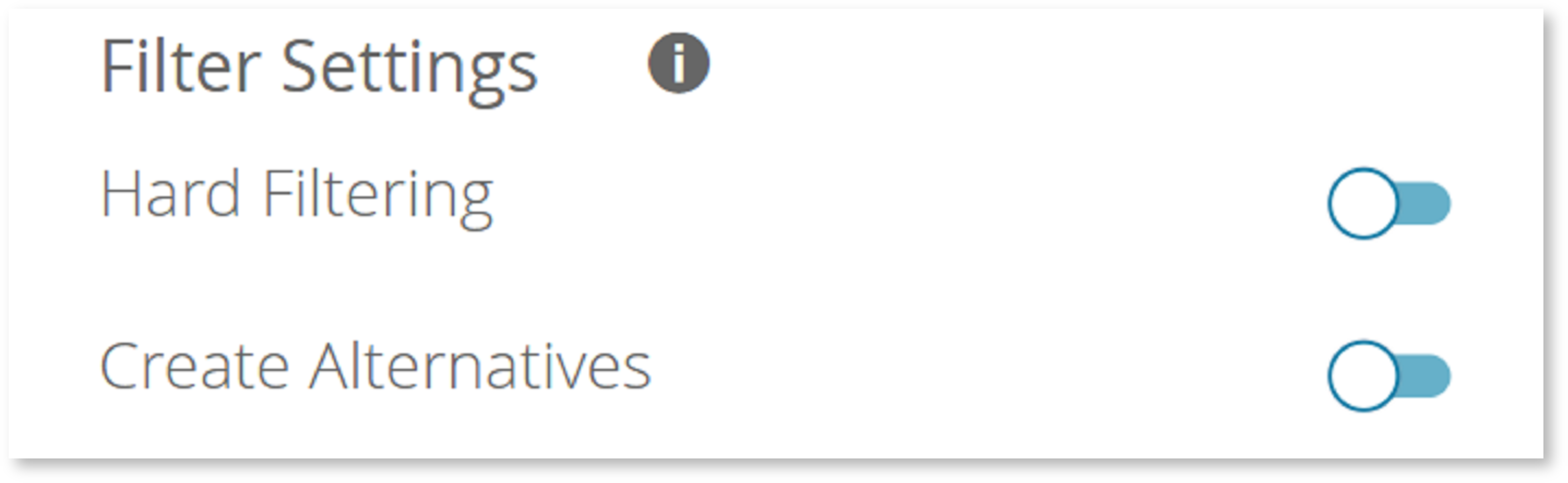
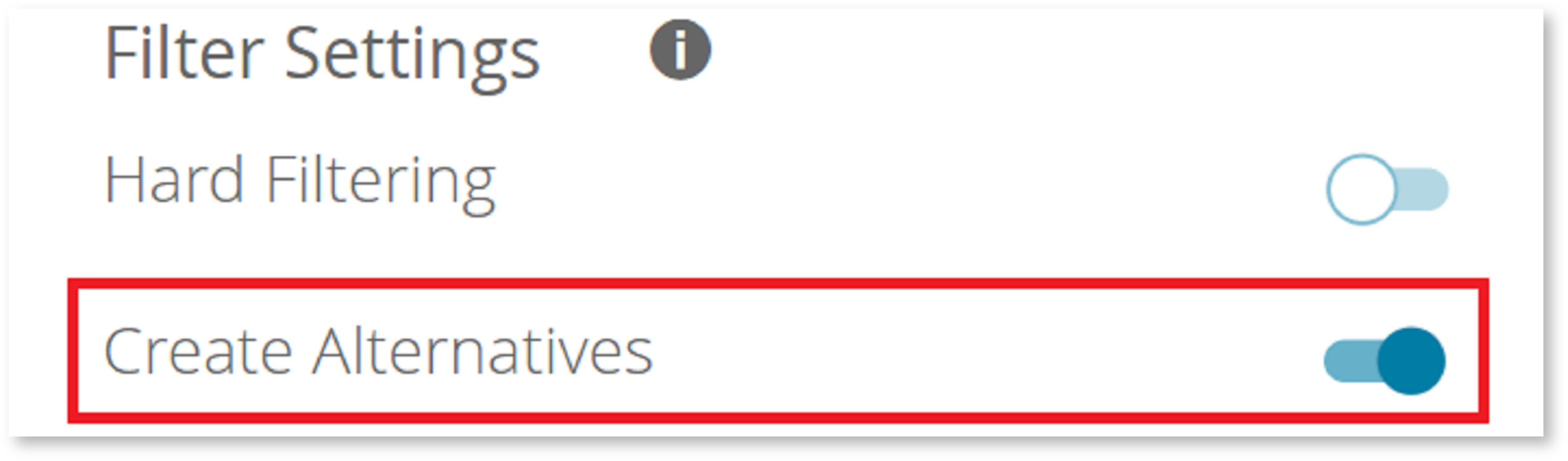
Filter Settings
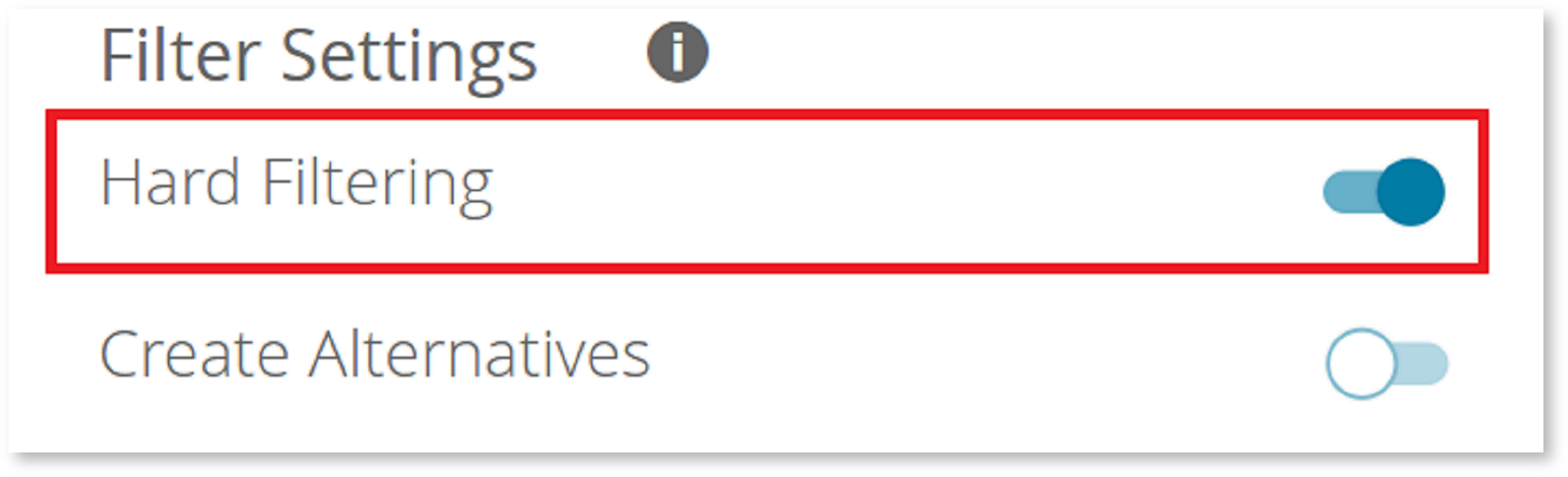
Furthermore, you can decide how the results of the Question should be represented in the product recommendation. That means that you can enable or disable a hard filtering. With an active hard filter all products which not fulfill the user-selected Answer Options are not shown in the recommended result list.
Filtering Opportunities | Settings and Description |
|---|---|
No Filter | No filter is set: A deactivated hard filter does not remove any products. The difference is that these products do not get any fitting points and as a consequence are ranked lower than products which fulfill these criterias. |
Hard Filter | A "hard filter" displays only the perfect matches in the recommendation page. |
Alternatives | "Create Alternatives" shown in result list (no perfect match) |
Use Case
(see Matching Use Case below).
Matching Logic
Only relevant for questions that allow the selection of multiple options by the user.
Given multiple selection options on the question the matching logic specifies the logical relation between the selected options - OR / AND
OR:
At least one of the selected answer options have to be fulfilled by a product to fulfill the user requirement.AND:
All of the selected answer options have to be fulfilled by a product to fulfill the user requirement.
Use Case
(see Matching Use Case below).
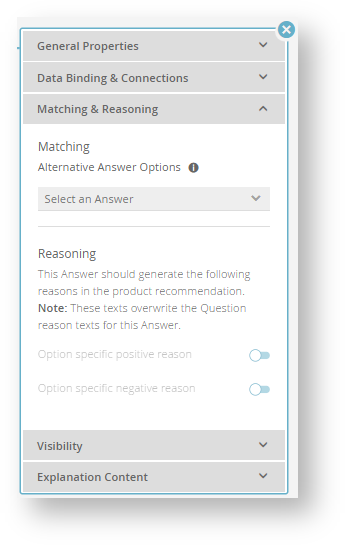
Alternative Answer Options
Given a particular answer option A you can define other alternative answer options X... to Z that if fulfilled as a requirement also qualify a product as being a valid recommendation for A.
Conclusions
There are no negative reason texts if the Alternative Answer Option was selected.
The fit score is lower than the score from the actual Answer Option. Thus products which fulfill the features of the chosen Answer Options are ranked higher than than products which only fulfill the alternative Answer Options.
The fit score is higher than the score from Answer Options which are not part of the alternative Answer Options or the actual Answer Option itself.
Use Case
(see Matching Use Case below).
Question Use case
These use cases for the settings for the Question help you to understand the presented settings.
Answer Option Use case
These use cases for the settings for the Answer Option help you to understand the presented settings.
Match Weight
The color has a low and the gender has a high match weight, thus the results in a higher score for products with the requested gender which further results in a higher spot in the product recommendation list.
The attribute color has set middle match weight: thus the products in result list is default. (like in product data)
Question | Which color? | Which type of break? |
|---|---|---|
Users Answers | blue | carbon |
Match Weight | 1 | 2 |
Filter Settings
The attribute color has set no filter: thus there is no filtering and all products are shown in result list. |
The attribute color has set Hard filtering: thus only products that have the chosen "color" are displayed in the results list. |
The attribute color has set Create Alternatives: thus also products which are non perfect matches (in this case: not the chosen color) are shown in result list. |
Filter Mode: Hard filter = OFF for both Questions
Product Result List | Color | Break Type | Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
P1 | blue | carbon | 3 = 1 + 2 |
P2 | green | carbon | 2 = 0 + 2 |
P3 | blue | steel | 1 = 1 + 0 |
P4 | green | steel | 0 = 0 + 0 |
Filter Mode: Hard filter = ON for the Question "Which color?"
Product Result List | Color | Break Type | Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
P1 | blue | carbon | 3 = 1 + 2 |
P3 | blue | steel | 1 = 1 + 0 |
Matching Logic
GOOD: Question about colors of a jacket with two selected Answer Options "blue" and "grey". The corresponding product attribute color has multiple values (e.g. "blue, grey", "green, black", etc.). Thus a product can be found that fulfills both color wishes.
BAD: Question about car brands with two selected Answer Options "Mercedes" and "Audi". All cars only have exactly one brand. That is why an "AND" logic would result in getting negative reasons for the not fulfilled brand. As a consequence there would not be any top recommendation.
Alternative Answer Options
The color could be "blue" or "marine". All variants are shades of blue but have different names. If you select the alternative answer option "marine" for the color "blue" then there is no negative reason if the user selects "blue" and the product has the color "marine".