With the aid of the Annotation view you are able to assign the attribute values, created in the Attribute Creation view, to your products. The following sections explain what you have to consider before, and what to do during the annotation process.
Table of Contents:
When you enter the Annotation view for the first time you can see the following elements:
Clicking on "Start Annotation" opens a modal window where you have to configure some settings. These settings help you during the annotation process, to decide which attribute value you should assign to each product. Read more about the settings on the page Annotation Settings.
When you start the annotation process the view looks something like this:
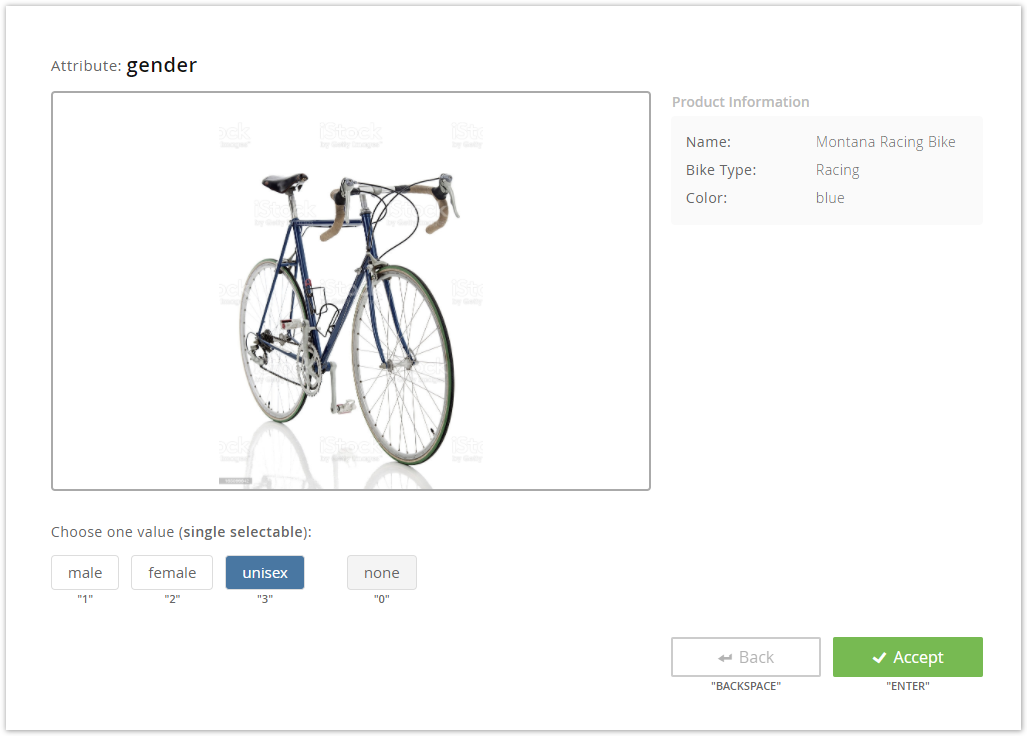
On the top you see your created attribute name. Below, the product image is displayed along with further product information which you set in the Annotation Settings.
Furthermore, the view control elements are available:
Attribute value selection:
Choose one or multiple values from the created attribute.
In case you are not sure which value to select and wish to skip annotating this product, you can select the value "none".
The value "none" represents an empty annotation. The AI model won't consider any of the products annotated as "none". In production, those products will be assigned an attribute value as predicted by the model.
|
You can also annotate the products without using the mouse. A label is displayed below all the control elements (e.g. "1" or "ENTER"). If you press this key on your keyboard the corresponding value is selected. This feature saves time and is more comfortable to use. |
The AI model isn't capable of learning any useful patterns if it doesn't observe enough data. Therefore, a minimum of 10 products must be annotated per attribute value. All attribute values with less corresponding products are simply ignored. At least two attribute values need to have enough annotations, otherwise it wouldn't make sense to train a model at all, since it would always predict the value with the most annotations. Thus any attempt to train a model with fewer annotations would fail. The minimal amount of annotations required to train an accurate model is highly dependent on the complexity of the attribute and the availability of informative data attributes to learn from. It is perhaps best to iteratively train new models and annotate further products until the desired model accuracy is reached. |
You can stop the annotation process anytime. There are multiple ways to end the annotation.
After stopping the annotation you are able to create a prediction model. As mentioned before, the rule applies: More product annotations result in a more precise prediction.
...