Table of Contents:
When to Use Continuous Numeric?
Continuous Numeric Questions are suitable if:
- The Data Binding of this Question is set to a data attribute of the type Number (actually, Continuous Numeric requires Number data attributes).
- The Numeric product attribute values don't have a fixed set of values, but the amount of values is variable and e.g. can change upon every update of the data feed (e.g. as for the price attribute).
Note: In the case of variable data attributes, it is impossible to manually map an Answer Option to one precise product value (or it requires an infinite number of Answer Options to reflect every possible occurrence).
- However, you can also use the Continuous Numeric Question with product attributes with a fixed set of values.
A great feature of Continuous Numeric Questions is that they can use steppings. Steppings define intervals or "ticks" in the widget (well known from a price slider widget that has e.g. steps at 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 €).
Requirements
- Answer Option data mapping has to be set to "Simple" (see Simple Mapping).
- Selected product attribute must have the type "Number" (see Upload your Product Data File).
Differences to Ordered Answer Option Type
| Continuous Numeric | Ordered | |
|---|---|---|
| Answer Options | There are no explicit Answer Options. They are defined with the aid of the Stepping Configuration. | Ordered Answer Options are manually created and defined by the user. |
| Product Attribute Type | Only type Number is allowed. | All types (Text, Number, Boolean) are possible. |
| Order of the Values | Order is implicit due to the numeric typing. | Order is defined by the sequence of the created Answer Options. |
| Proportion of the Values | Due to the numerical values the proportion/distance is clearly defined. Therefore e.g. 100 is twice as much as 50. | One Answer Option can define intervals e.g. "25 to 50" and "50 to 100". These intervals are written as text and therefore can not be interpreted in the same way as the Continuous Numeric type. |
Further notes
Some of the following points are connected to the requirements:
- You cannot change the answer option data mapping.
- The product attribute can only be changed to attributes which also have the type "Number". Otherwise an error message occurs and the selection is reverted.
- Changing the product attribute type from "Number" to "Text" in the product data view causes a modal window to show up. By confirming this message the connection between the attribute and the continuous numeric question will be dissolved.
- The property "The user can select one answer/several answers" in the "General Properties" tab will be disabled and per default set to "one answer". This is needed because the selection of more than one answer isn't possible for this type of question. This is also valid for range selections because the range is interpreted as one answer. Multiple answers would represent multiple ranges which isn't possible at the moment.
- If the answer option type is changed to another type, the continuous numeric question layout will be changed to a "normal" or boolean question layout (see Boolean Question).
- No answer options can be added or deleted.
Creating a Continuous Numeric Question
Example
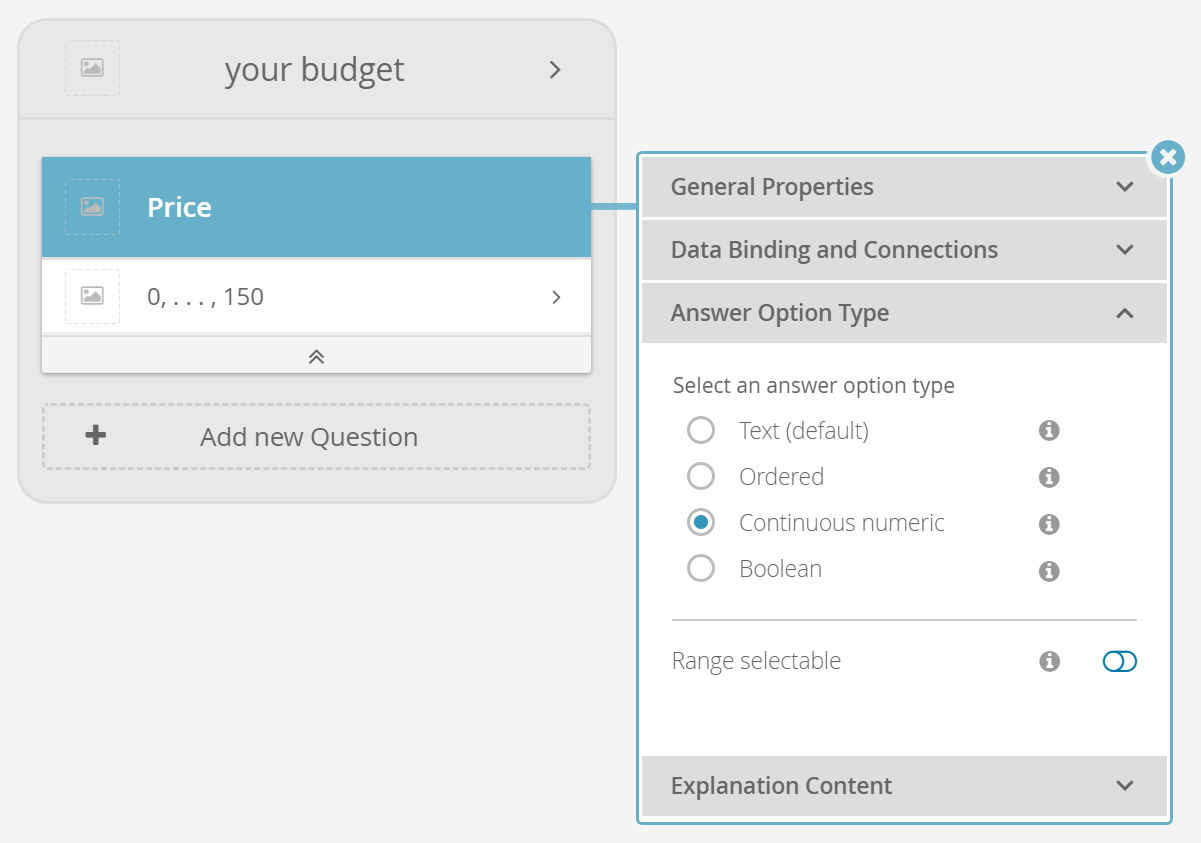
A typical example of Continuous Numeric Question is the request of the price (see image below). The next section describes the steps to create this type of Question.
Further examples of Questions that might use Continuous Numeric:
- Weight in kg
- Size in cm
Configuration Steps
- We assume that you have a Question card "Price" which is connected to the numeric product attribute "Price". This Question can perfectly converted into a Continuous Numeric Question.
Note: Make sure that the product attribute has the type "Number" (see Data Attribute Table).
- Go to the tab "Answer Option Type" and select the type "Continuous Numeric". If this option is disabled the connected product attribute is not from type "Number".
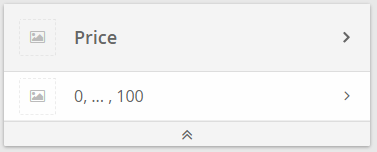
- The Question card appearance transforms. There is one Answer Option card which represents the Stepping Configuration. More precisely it shows the start and the end value separated by dots to symbolize that there are several value between these values.
- Afterwards you can configure the stepping intervals which are described in the next section.
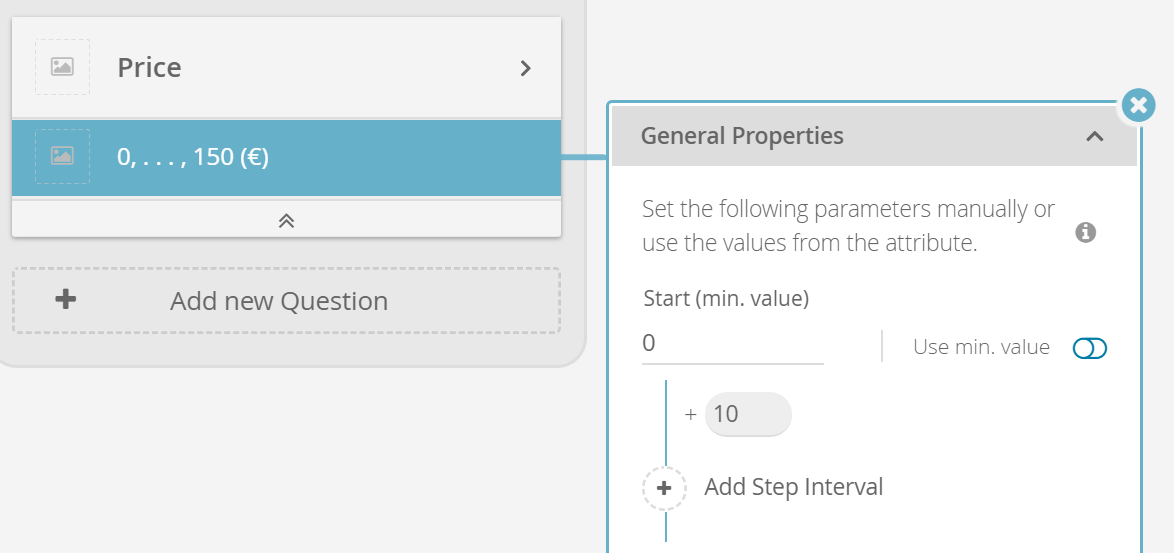
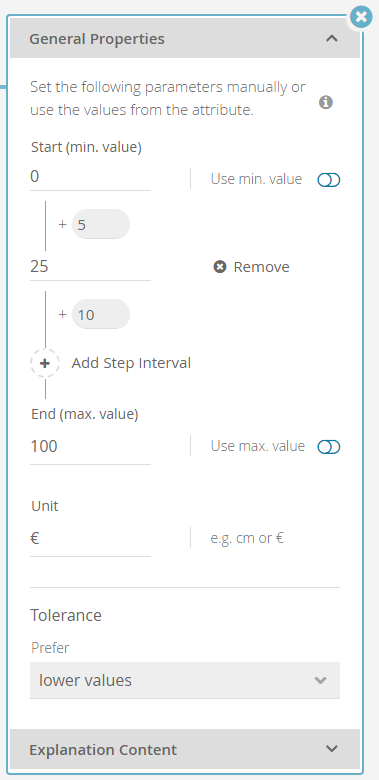
Configure the Stepping of Numeric Values
The Stepping feature allows you to add and configure steps for numeric values. Steps means i.e. "ticks" or "stop points" where a specific value can be selected.
This is an important feature because attributes like e.g. price could have hundreds of different values in your product data feed. Normally you want to have a fix number of steps in a price slider or number picker widget and don't want to change it in an unintended way if the prices in the product data change.
To enter the stepping configuration dialog, just click on the Answer Option box of a Question (i.e. here the box showing "0, ...., 150 (€)":